Tag: eye color
Do Adult Red-tailed Hawks Always Have Dark Eyes?
Northern Harrier Photos With A Shared Flaw
Female Hooded Merganser With A Hammerhead Reflection
Cormorant Eyes
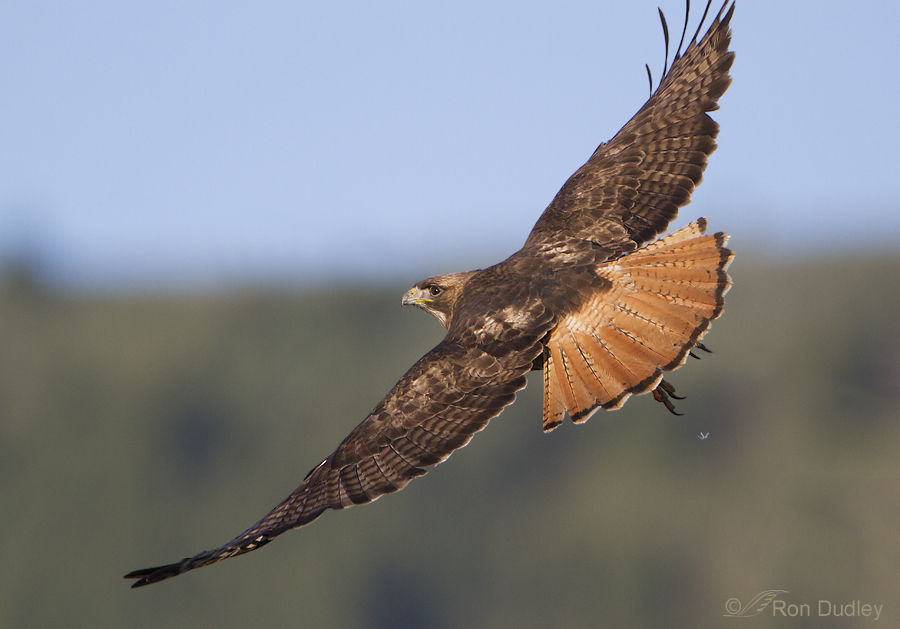
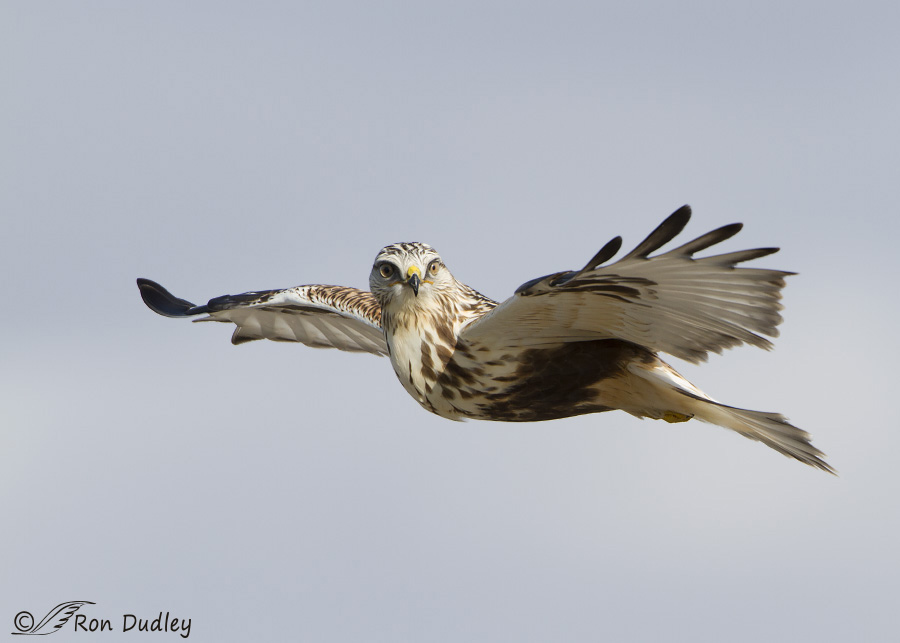
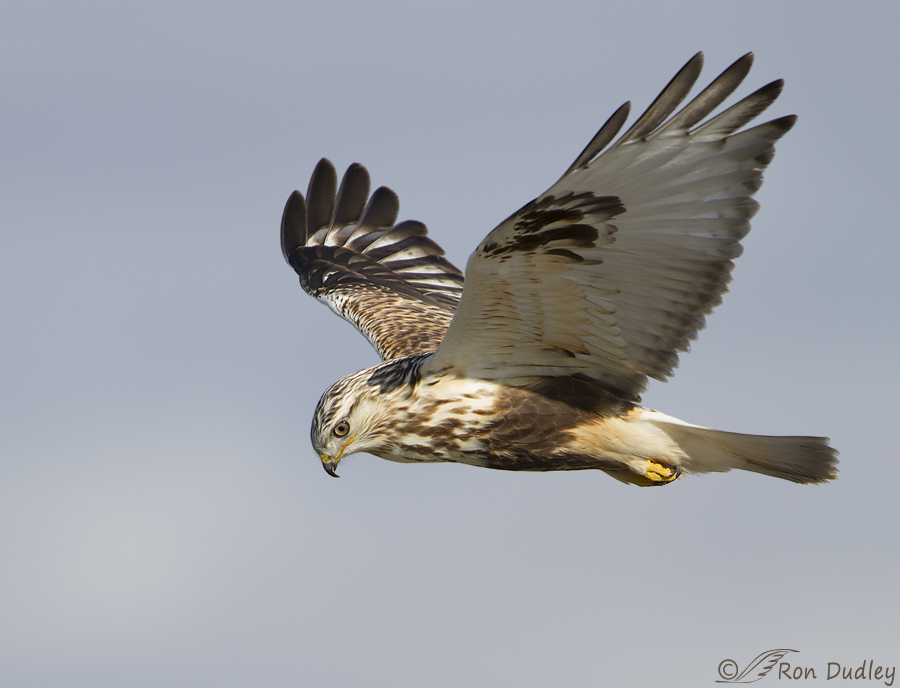
Sexing (and identifying juvenile) Rough-legged Hawks
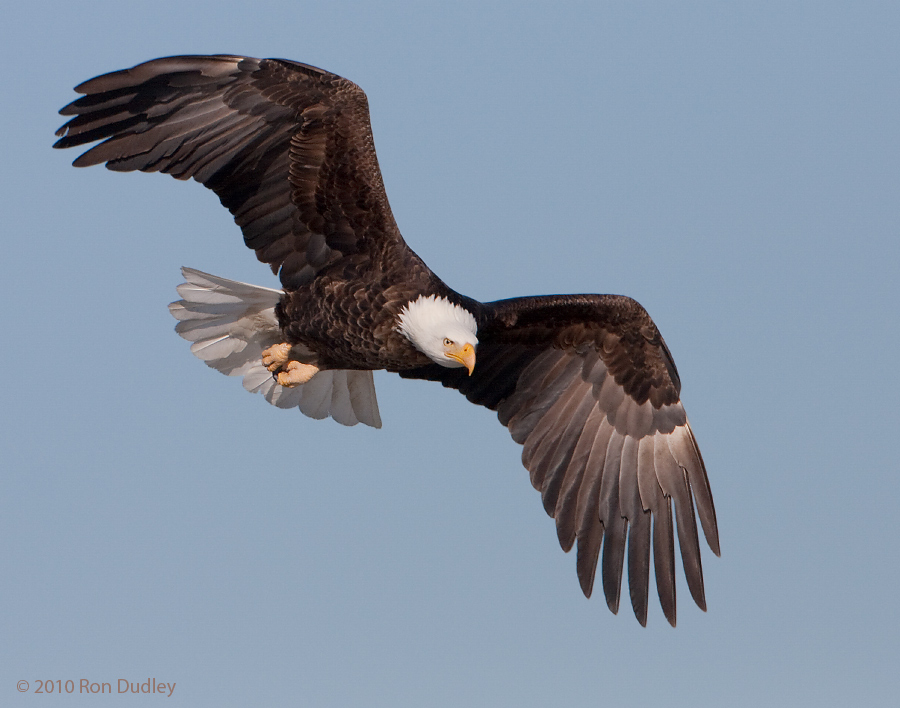
A Guide To Aging Bald Eagles And How To Distinguish Immature Bald Eagles From Golden Eagles
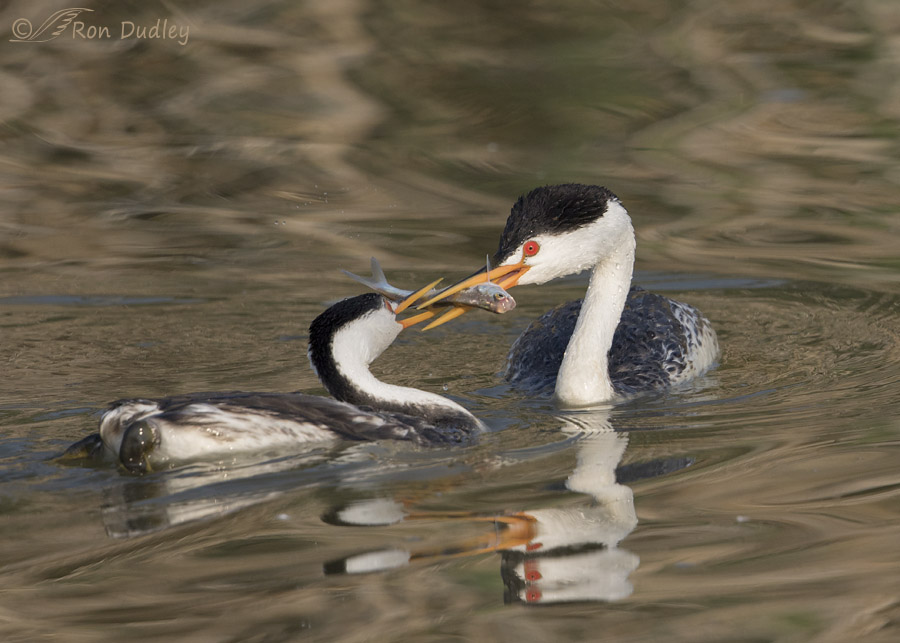
Clark’s Grebe Trying To Feed A Fish To A Reluctant Juvenile
Rough-legged Hawk – Hopefully A Harbinger Of Birds Soon To Come
A Guide To Aging Bald Eagles
As we go into prime “eagle watching” season here in northern Utah I thought it might be timely to present a guide that would be helpful in aging Bald Eagles as they progress through the 5-6 year process of becoming adults. Many of these younger birds are mistakenly identified as Golden Eagles by the general public. Eagles that have not reached the adult stage are referred to as immature, juveniles or sub-adults. Plumage stages are highly variable, depending on molt sequence, age and timing so other factors like iris and beak color are also taken into account when estimating age. Eyes gradually change from dark brown to yellow while the beak goes from blackish-gray to yellow. 1/4000, f/8, ISO 500, 500 f/4, not baited, set up or called in The adult Bald Eagle is unmistakable with its distinctive bright white head and tail contrasting with the dark brown body and wings. 1/200, f/6.3, ISO 800, 500 f/4, 1.4 tc, not baited, set up or called in But juveniles present very differently than adults, especially in the early stages of development. This very young bird is barely fledged and was still hanging around its nest in sw Montana. Notice that the plumage is dark brown throughout, though they may have some white or pale mottling at this stage – especially on the underparts. Both eye and beak are very dark. 1/2000, f/6.3, ISO 500, 500 f/4, 1.4 tc, not baited, set up or called in This is a first year bird during winter. 1/800, f/8, ISO 500, 500 f/4, natural light,…