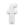Juvenile Red-tailed Hawk
For several days early last month I was able to photograph this juvenile Red-tailed Hawk (and occasionally its apparent sibling) while it was “sit and wait” hunting for voles from elevated rocks on Antelope Island. The first six images I’ve presented here were all taken on the same morning. 1/2000, f/7.1, ISO 400, 500 f/4, 1.4 tc, natural light, not baited, set up or called in Many of these shots were taken during or just after take-off and you’ll notice that the bird was flying to my left in all six images taken that morning. That’s due to the “lay of the land” and the fact that the rocks this bird was hunting from were angled on the side of the mountain in such a way that the hawk was always hunting an area to my left. This is one of the few times the bird took off when it wasn’t after prey. 1/3200, f/6.3, ISO 400, 500 f/4, natural light, not baited, set up or called in When the hawk had spotted prey before it took off it never took its eyes off the quarry as it was going in, so I normally wouldn’t get direct eye contact. This bird was very close when it took off – you’ll notice from my techs that I’d removed my tc and the hawk was still quite large in the frame. 1/2000, f/6.3, ISO 500, 500 f/4, 1.4 tc, natural light, not baited, set up or called in It was somewhat problematic when there were rocks directly behind the…